研究
研究テーマ
- 裸地斜面における凍結融解による土砂生産に関する検討および土石流発生状況の現地観測
- 融雪型火山泥流発生機構に関する研究
- 掃流砂計測手法の開発
- 表層崩壊解析手法の検討
- 火山地帯における降雨流出機構
- 山岳河川におけるフラッシュフラッド発生機構
- TDRを用いた流砂観測手法の開発
- 排砂実験
- 天然ダムの越流、決壊に関する現地大規模実験
裸地斜面における凍結融解による土砂生産に関する検討および土石流発生状況の現地観測
凍結融解により風化した岩盤が破壊され新たに土砂が生産される現象は、流域全体に分布する裸地において恒常的に起こり、冬期に一般的に見られる現象である。この種の土砂生産は、対象地域の気候や地質、地形に依存する現象で、長期的な視点から、山地斜面から河道へ供給される土砂生産のポテンシャルを表わしていると解釈することができる。流域全体の裸地分布、気候、地形から長期的な土砂生産ポテンシャルを計算し、それを流域全体の土砂生産量の推定に用いることは比較的容易で有効な手段になりうる。これまで、冬期の凍結融解に関する現地観測や熱伝導解手法により岩盤の凍結融解をシミュレートし流域全体からの土砂生産量の推定方法の開発等を行っている。

また、凍結融解等によって生産され斜面脚部に堆積した土砂は、その後の降雨に際し、土石流の発生場となり得る。土石流発生に関する研究では多くの場合、土層の飽和度は一定として検討がなされているが、実際の土石流発生域での観測事例は,土石流の発生時に土層が全層にわたって飽和していない可能性が指摘されている。土石流発生域とみなされるヒル谷源頭部の渓床堆積物に関して継続的な観測を行い、土砂移動発生時の水分動態を捉えるための現地観測等を継続的に実施している。
参考文献はこちら
- Tsutsumi, D., Fujita, M. (2016): Field observations, experiments, and modeling of sediment production from freeze and thaw action on a bare, weathered granite slope in a temperate region of Japan, Geomorphology, 267, 37-47.
- 泉山寛明,堤大三,藤田正治(2015):地質を考慮した風化基岩における凍結融解による土砂生産量の推定方法,砂防学会誌,68(5),10-20.
- 堤大三,藤田正治,竹門康弘,角哲也,泉山寛明(2014):木津川流域の土砂生産ポテンシャルの推定,砂防学会誌,66(5),13-22.
- 速見智,里深好文,藤本将光,堤大三(2014):山地源頭部における渓床堆積物中の水分動態および土砂流出に関する研究,第7回土砂災害に関するシンポジウム論文集,211-216.
- 速見智,里深好文(2013):山地源頭部における渓岸堆積物の水分動態と土砂移動の観測,土木学会論文集B1(水工学),69,I_943-I_948.
- Izumiyama, H., Tsutsumi, D., Fujita, M. (2012): Effect of Freeze-Thaw Action on Porosity Change and Destruction of Weathered Bedrock in Different Lithology and Development of Destruction Model, International Journal of Erosion Control Engineering, 5(1), 103-112.
- 泉山寛明,堤大三,藤田正治(2012):間隙構造の変化を考慮した風化基岩の凍結融解時における熱伝導と水分移動の解析,土木学会論文集B1(水工学),68(4),I_529-I_534.
- 泉山寛明,堤大三,藤田正治(2011):裸地斜面の凍結融解強度に積雪および地形特性が与える影響,水工学論文集,55,715-720.
- 堤大三,藤田正治,泉山寛明(2009):気温上昇による土砂生産に対する凍結融解の影響変化予測,水工学論文集,53,649-654.
- 泉山寛明,堤大三,手島宏之,藤田正治(2009):地表面熱収支を考慮した裸地斜面における凍結融解シミュレーション,水工学論文集,53,643-648.
- 水谷太郎,里深好文,堤大三,水山高久(2008):急勾配渓床堆積物中の水分移動,砂防学会誌,61(3),27-30.
- 堤大三,藤田正治,伊藤元洋,手島宏之,澤田豊明,小杉賢一朗,水山高久(2007):凍結融解による土砂生産に関する基礎的研究―田上山地裸地斜面における現地観測と数値シミュレーション―,砂防学会誌,59(6),3-13.
- 堤大三,藤田正治,澤田豊明,伊藤元洋,手島宏之(2006):滋賀県南部田上山地における凍結融解と土砂生産に関する観測,京都大学防災研究所年報,49,567-573.
- Tsutsumi, D., Fujita, M., Teshima, H. (2006): Field Observation and Numerical Simulation for Sediment Yield due to Freeze and Thaw Process, The 6th Japan-Taiwan Joint Seminar on Natural Hazard Mitigation
融雪型火山泥流発生機構に関する研究
焼岳の冬期の積雪は最大で10 m近くになる場所もある。一方、噴火時の噴出物は数100℃、時に1000℃に達する高温になることがあると考えられている。これら高温の火山噴出物が、山全体を覆う積雪の上に降り積もると,短時間で雪を融かし、大量の水と土砂が泥流となって流れ下る事が起こりえる。この現象は「融雪型火山泥流」と呼ばれ、防災の観点から非常に恐ろしい現象と考えられる。この融雪型火山泥流による災害を防止・軽減するため、数値シミュレーションの予測精度向上と、その結果としてのハザードマップの信頼性向上を目的として、現地実験および融雪過程のモデル化を行っている。
また、融雪型火山泥流発生過程のモデル化において必要な、積雪層内の融雪速度と浸透速度の大小を決定する条件や、融雪出水量に対し影響が大きいと考えられる含水量、積雪密度の時系列変化を知るため、土木研究所との協力のもと現地観測を行っている。
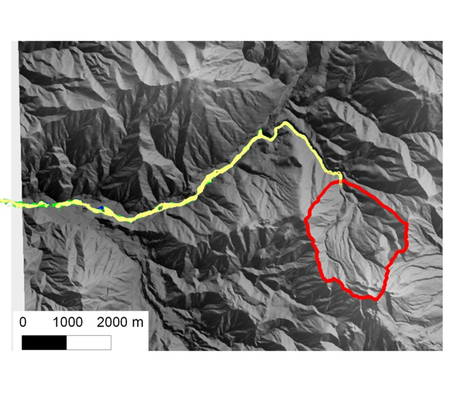
噴火による融雪に伴う泥流は,発生事例が少なく、発生過程について不明な点も多い。しかし、数値シミュレーションによる予測精度の向上のためには、発生する泥流の規模とタイミングを予測する必要がある。発生過程について、融雪過程のモデルと取り入れ、さらに融雪水の浸透,流下とそれに伴う斜面崩壊の発生などを考慮し、泥流発生過程のモデル化を行っている。ここで得られた発生泥流のハイドログラフを2次元の泥流モデルの入力条件として、泥流の到達範囲やタイミングについてシミュレーションを行っている。
参考文献はこちら
掃流砂計測手法の開発


山地流域における土砂動態に関して、観測される流砂量は土砂生産・供給源の規模や季節変動に依存し、河川流量のみに依存するわけではないことが知られている。このため、流域の総合的な土砂管理や、土砂・河川災害の防止・軽減のためには、流砂量の実測が不可欠である。最近では、間接的な計測手法として、音響センサーを利用したパイプ式ハイドロフォンやスイスにおいて開発されてきた、プレート式ジオフォンによる掃流砂観測手法が広く用いられるようになった。
それぞれの計測手法は、基本構造や用いるセンサーの違いから、それぞれの利点や欠点があるが、これまでは定量的な比較検討がなされてこなかった。当観測所ではSwiss
Federal Institute WSLとの共同のもと、足洗谷観測水路とスイスのErlenbachにおいて、パイプ式ハイドロフォンとプレート式ジオフォンの双方を設置し、掃流砂観測における観測結果の比較検討を行っている。また、従来の水平型ハイドロフォンに加え、鉛直型のハイドロフォンを設置した新たな計測手法についても検討を進めている。その他に、日本工営株式会社との共同のもと、荷重計型の掃流砂観測装置の開発を行っている。
参考文献はこちら
- 東豊,堤大三,宮田秀介,藤田正治(2022):パルス法による山地河川における流砂量推定手法の高度化,砂防学会誌,74(5),3-13.
- Ito, T., Nagayama, T., Utsunomiya, R., Fujita, M., Tsutsumi, D., Miyata, S., Mizuyama, T. (2018): Development of new sensor systems for continuous bedload monitoring using a submerged load-cell system (SLS), Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 43(8), 1689-1700.
- Ito, T., Nagayama, T., Utsunomiya, R., Fujita, M., Tsutsumi, D., Miyata, S., Mizuyama, T. (2017): Development of a bedload sensor for continuous measurement and its applicability, River Sedimentation - Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on River Sedimentation, ISRS 2016, 239-245.
- 長谷川祐治,宮田秀介,今泉文寿,中谷加奈,堤 大三(2017):流砂の衝突回数を考慮したハイドロフォンデータによる解析手法の提案と現地への適用,土木学会論文集B1(水工学),73(4),I_523-I_528.
- Ito, T., Gotoh, K., Utsunomiya, R., Nonaka, M., Nagayama, T., Tsutsumi, D., Fujita, M., Miyata, S., Mizuyama, T. (2014): Experimental studies for monitoring of bedload using various sensors, Symposium Proceedings of INTERPRAEVENT2014 in the Pacific Rim, O-17, 1-10.
- Koshiba, T., Auel, C., Tsutsumi, D., Kantoush, S.A., Sumi, T. (2018): Application of an impact plate – Bedload transport measuring system for high-speed flows, International Journal of Sediment Research, 33(1), 35-46.
- Tsutsumi, D., Higashi, Y., Nonaka, N., Fujita, M. (2017): Bedload monitoring in a mountain stream method for improving the accuracy of the calibration relationship between acoustic pulses and bedload discharge, 2nd International workshop on sediment bypass tunnels.
- Goto, K., Itoh, T., Nagayama, T., Utsunomiya, R., Tsutsumi, D., Mizuyama, T. (2016): Development and installation of bedload monitoring systems with submerged load cells, Journal of Mountain Science, 13(2), 369-376.
- 小柴孝太,角哲也,堤大三(2016):プレート型振動センサを用いた掃流砂量計測手法に関する研究 ,土木学会論文集B1(水工学),72(4),I_925-I_930.
- 谷寧人,堤大三,水山高久(2012):流砂観測に基づく土砂移動特性の評価及び土砂供給減の推定,砂防学会誌,65(3),21-28.
- Mizuyama, T., Hirasawa, R., Kosugi, K., Tsutsumi, D., Nonaka, M. (2011): Sediment monitoring with a hydrophone in mountain torrents, International Journal of Erosion Control Engineering, 4(2), 43-47.
表層崩壊解析手法の検討
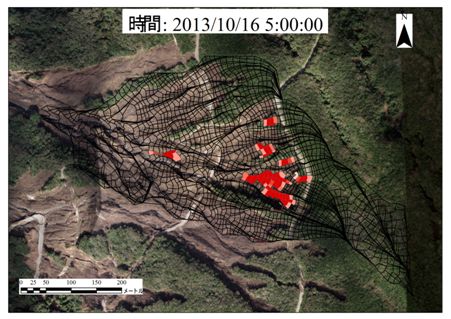
豪雨に伴って発生する表層崩壊についての解析手法を検討している。近年発生した表層崩壊(2012年の阿蘇山周辺、2013年の伊豆大島、2014年の広島等)は、崩壊発生域が広範囲に及んでおり、単一斜面を対象としたシミュレーション手法では対応できない。一方で、流域単位を対象とした既往の分布型の崩壊予測モデルでは、相対的な斜面安全率を算出することによって危険度を判定できるものの、崩壊発生のタイミングや土砂量までは推定できず、その後の土砂流出現象へ解析を繋げることができない。そこで、地形データを元に流域をトポチューブによって分割し、それぞれ単独のチューブに対して降雨流出モデルによって斜面土層内の地下水位を計算し、その結果を臨界すべり面探査手法を用いた斜面安定解析に入力値として用いて、斜面安全率を求める崩壊予測モデルを開発している。
参考文献はこちら
- 堤大三(2020):土層内の浸透流解析にパイプ等による選択流を組込んだモデル,地下水学会誌,62(3),363-382.
- 山野井一輝,堤大三,藤田正治(2020):ストリームチューブに基づく地形分割を用いた斜面崩壊と土砂流出の統合シミュレーション,土木学会論文集B1(水工学),76(2),I_889-I_894.
- 堤大三,孝子綸図,山野井一輝,藤田正治(2019):ストリームチューブによる地形分割を基にした表層崩壊解析手法,砂防学会誌,72(2),3-13.
- 堤大三,藤田正治,宮本邦明,今泉文寿,藤本将光,国領ひろし,泉山寛明(2011): 台湾高雄県小林村の深層崩壊発生機構に関する解析,土木学会論文集B1(水工学),67(4),I_721-I_726.
- Tsutsumi, D, Satofuka, Y, Hotta, N, Fujita, M, Miyata, S (2011): Landslides Induced by TohokuPacific Ocean Earthquake, 2011, Proceeding of 2nd INternational Workshop on Multimodal Sediment Disaster - Asian Cloud Network on Disaster Research-, 27-139.
- Fujita, M., Ohshio, S., Tsutsumi, D. (2010): A prediction method for slope failure by means of monitoring of water content in slope-soil layer, Journal of Disaster Research, 3(5), 296-308.
- 堤大三,藤田正治(2008):斜面崩壊過程に与える土層の物理特性の影響に関する検討,水工学論文集,52,565-570.
- 多田泰之,藤田正治,堤大三,小山敢,河合隆行,奥村武信,本田尚正(2007):地中水みちと崩壊発生位置の関連性,砂防学会誌,60(4),25-33.
- 堤大三,藤田正治,林雄二郎(2007):2005年台風14号により大分県竹田市で発生した斜面崩壊に関する数値シミュレーション,水工学論文集,51,931-936.
- 多田泰之,藤田正治,堤大三,小山敢,河合隆行(2006):地下流水音による地中水みち経路の推定,水工学論文集,50,283-288.
- Tsutsumi, D., Sidle, R.C., Kosugi, K. (2005): Development of a simple lateral preferential flow model with steady state application in hillslope soils, Water Resources Research, 41(12), W12420.
- 藤田正治,里深好文,堤大三,多田泰之(2005):2004年三重県宮川村および徳島県木沢村の斜面崩壊プロセス,京都大学防災研究所年報,48(B),625-630.
- 堤大三,藤田正治,SIDLE Roy C,林雄二郎(2005):風化基岩中の選択流を考慮した浸透計算と斜面安定解析,京都大学防災研究所年報,48(B),631-637.
- 堤大三, 宮崎俊彦, 藤田正治, SIDLE Roy C(2005):パイプ流に関する数値計算モデルと人工斜面実験による検証,砂防学会誌,58(1),20-30.
- 堤大三,藤田正治,Roy C. Sidle(2005):基岩クラックを通した選択流と斜面安定性に関する数値実験,水工学論文集,49,1039-1044.
- 堤大三,Roy C. SIDLE,藤田正治,小杉賢一朗(2004):斜面土層内のパイプによる選択流のモデル化,京都大学防災研究所年報,47(B),151-159.
- 堤大三,Sidle R.C,藤田正治,水山高久(2004):パイプ流存在下での斜面の安定性に関する数値実験,水工学論文集,48(1),337-342.
火山地帯における降雨流出機構

火山がひとたび噴火すると、火山噴出物(火山灰、火砕流堆積物など)によって山腹斜面が覆われ、土石流の発生頻度および規模が激増する危険性がある。これは、火山噴出物による浸透の阻害や植生の衰退が原因と考えられる。噴火後は降雨-流出過程が噴火前とはまったく変わってしまうことを意味する。したがって、流出特性の変化を考慮し、噴火後の土石流発生予測を行わなくてはならない。一方、斜面を覆った火山噴出物は、物理的、化学的な変化により、時間の経過とともに浸透特性が変化すると考えられる。そこで、非常に噴火頻度の高い桜島と2010年に大規模噴火が起こったインドネシア・Mt. Merapiを対象として、現地実験、現地観測を実施し、噴火に伴う流域特性の変化を考慮した水文モデルの開発を進めている。
参考文献はこちら
- 平川泰之,岡野和行,植野利康,里深好文,堤大三,宮田秀介(2019):噴火後20年を経過した雲仙普賢岳の火砕流堆積斜面における土石流発生を助長する地形・地質的条件,砂防学会誌,72(1),21-31.
- Gonda, Y., Miyata, S., Fujita, M., Legono, D., Tsutsumi, D. (2019): Temporal Changes in Runoff Characteristics of Lahars after the 1984 Eruption of Mt. Merapi, Indonesia, Journal of Disaster Research, 14(1), 61-68.
- 平川泰之,岡野和行,植野利康,堤大三,宮田秀介,里深好文(2018):雲仙岳の噴火後20年を経過した火砕流堆積斜面における土石流発生場の地形・地質特性,砂防学会誌,71(3),12-20.
- Gonda, Y., Miyata, S., Fujita, M., Legono, D., Tsutsumi, D. (2018): Temporal changes of rainfall-runoff relationship after the 1984 eruption of Mt. Merapi, Indonesia, Proceedings of the 21th IAHR-APD Congress, 1277-1283.
- Masaoka, N., Kosugi, K., Katsuyama, M., Mizuyama, T., Miyata, S., Tsutsumi, D. (2014): Effects of bedrock groundwater and geological structure on hydrological processes in mountainous watersheds, Symposium Proceedings of INTERPRAEVENT2014 in the Pacific Rim, P-25, 1-7.
- 宮田秀介,藤田正治(2013):レーダ雨量を用いた流出シミュレーションと桜島における土石流発生渓流への適用,京都大学防災研究所年報,56(B),457-464.
山岳河川におけるフラッシュフラッド発生機構

急峻な山岳河川においてフラッシュフラッド(鉄砲水)と呼ばれる急激な出水による災害事例がしばしば報告されている。数分~30分の間に河川水位が数十~100cmと急激に上昇する出水現象であり、このような現象は、当該箇所で降雨が無いもしくは弱いときにも発生することがある。そのため、避難が間に合わす、河川利用者(ハイキングや魚釣り,登山者)が被害を受ける事例が起こる。そこで、神通川水系金木戸川を対象として、現地観測と数値シミュレーションを組み合わせることで、フラッシュフラッドの発生機構の解明および渓流ごとの発生危険度に関する指標の検討に取り組んでいる。
参考文献はこちら
- Hairani, A., Rahardjo, A.P., Legono, D., Istiarto, Miyata, S. (2018): Spatially distributed evaluation of initiation of mass erosion, Proceedings of the 21th IAHR-APD Congress, 1139-1144.
- 宮田秀介,藤田正治,堤大三,市田児太朗(2014):神通川水系金木戸川における水文観測-フラッシュフラッド現象の解明を目指して-,砂防学会誌,66(5),92-95.
- Miyata, S., Fujita, M., Teratani, T., Tsujimoto, H. (2014): Flash flood due to local and intensive rainfall in an alpine catchment, Symposium Proceedings of INTERPRAEVENT2014 in the Pacific Rim, O-33, 1-8.
TDRを用いた流砂観測手法の開発

山地流域における流砂量は河川流量のみに依存するわけではないことが知られている。そのため、流域の総合的な土砂管理や、土砂・河川災害の防止・軽減のためには、観測による山地河川での流砂量の把握が不可欠である。これまで、多くの流砂観測手法が提案されているが、それぞれ利点と欠点をもつため、観測対象河川の特徴にあった手法を用いる必要がある。一方、堆砂池や空き容量のある堰堤上流などでは、堆積土砂量を連続観測することで、流砂量を求めることができる。そこで、土壌水分計測などに用いられるTDR(Time Domain Reflectometry:時間領域反射測定法)を利用し、水面下の堆積土砂面形状(河床位)および堆積土砂の固相率を計測するシステムの開発を進めている。
参考文献はこちら
- 宮田秀介,野中理伸,靏本孝也,上小牧和貴,岩男忠明,藤田正治(2021):TDRセンサーを用いた土石流の間隙流体土砂濃度の現地観測,砂防学会誌,74(4),42-47.
- Miyata, S., Mizugaki, S., Naito, S., Fujita, M. (2020): Application of time domain reflectometry to high suspended sediment concentration measurements: laboratory validation and preliminary field observations in a steep mountain stream, Journal of Hydrology, 585, Article 124747.
- 内藤秀弥,宮田秀介,岸本昌之,服部浩二,石塚忠範,永田葉子,小菅尉多,藤田正治(2018):TDRによる土砂濃度計測を用いた山地河川での浮遊砂鉛直分布の観測,砂防学会誌,71(4),3-12.
- Miyata, S., Fujita, M. (2018): Laboratory based continuous bedload monitoring in a model retention basin: Application of time domain reflectometry, Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 43(9), 2022-2030.
- 宮田秀介,藤田正治(2015):TDR(時間領域反射測定法)を利用した堆積土砂面位および空隙率測定,砂防学会誌,68(1),32-38.
排砂実験

山地河川の流砂現象とそれに伴う河床の変動については、過去に様々な計測手法が提案されており、近年にも、技術の発展を取り入れて新たな手法が提案されてきている。手法ごとに計測に適する地形などが異なるため、新たな手法は計測可能な場を広げることにつながる。そこで、ヒル谷試験堰堤において試験的に排砂を実施し、新規手法や既存手法を相互比較することで、それぞれの適用可能範囲を明らかにし、改善に向けた検討を行っている。この研究は、計測手法開発や山地河川での土砂動態、河床地形変化を研究するグループと共同で行っている(東京大学、新潟大学、静岡大学など)。
参考文献はこちら
天然ダムの越流、決壊に関する現地大規模実験
大規模な斜面崩壊や土石流によって河道が閉塞し貯水池が形成される天然ダムは、その後の越流や決壊によって大規模な土砂流出が発生し、激甚な土砂災害を引き起こす恐れがある。このような天然ダムの決壊過程について現地実験した例は少ない。本観測所では、立命館大学と共同のもとヒル谷において自然河川を土砂でせき止めて人為的に天然ダムを作成し、その後の越流、決壊と土砂流出過程についての大規模現地実験を行っている。
参考文献はこちら
研究報告
文部科学省:学校施設の防災力強化プロジェクト(平成28年度)成果報告書
文部科学省の「学校施設の防災力強化プロジェクト(平成28年度)」を受諾し、「栃尾小学校における土砂災害に対する警戒避難のための観測プロジェクト」というテーマにて事業を実施しました。